Over-the-counter (OTC) sales of male sexual enhancement products among community pharmacists in Ogun State, Nigeria
Main Article Content
Abstract
Background: Over-the-counter sales of male sexual enhancement products is a global concern, particularly in developing countries. Community pharmacists are well positioned to prevent the misuse and abuse of such products.
Objective: To investigate the extent of over-the-counter sales of male sexual enhancement products by community pharmacists in Ogun State.
Methods: A descriptive cross-sectional study was carried out among community pharmacists in Ogun State using a convenience sampling technique. Data was collected using a semi-structure self-administered questionnaire and analysed using Statistical Package for Social Sciences (SPSS) version 20.0 with statistical significance set at p =0.05. Results were presented as frequency tables and charts.
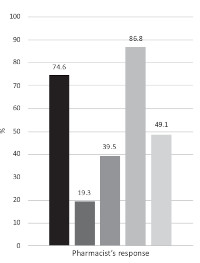
Results: Most respondents sold male sexual enhancement products on a daily basis, particularly sildenafil (64.9%) and tadalafil (50.0%). Highest proportion of the respondents (86.8%) sold the products without prescription but offered medication counselling, while 19.3% asked for a prescription before selling the products. About 46% sold the products over-the-counter based on the assumption that the users were conversant with the products. Additional qualification and monitoring of sales over the counter (p=0.03) were both significantly associated with over-the-counter sales of male sexual enhancement products.
Conclusion: Sales of male sexual enhancement products over-the-counter is a common practice among community pharmacists in Ogun State.
Downloads
Article Details
Issue
Section

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 International License.
How to Cite
Share
References
Bhagavathula AS, Elnour AA and Shehab A (2016). Pharmacovigilance on sexual enhancing herbal supplements. Saudi Pharmaceutical Journal 24;115-118.
Suleiman AK, Khan TM, Emeka PM, Ahmad S and Mansoor SM (2016). The public purchase of aphrodisiac products without prescriptions in the Alahsa region of KSA. Journal of Taibah University Medical Sciences, 11(5):413-417.
Morales AM, Ibanez J, Machuca M, Pol-Yanguas E, Schnetzler G and Renedo VP (2010). The EPIFARM study: an observational study in 574 community pharmacies in Spain characterizing patient profiles of men asking for erectile dysfunction medication. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 7:3153-60.
Morales AM, Hatzichristou D, Ramon Lladós J, Pascual Renedo V, and Pimenidou A (2013). Community pharmacy detection of erectile
dysfunction in men with risk factors or who seek treatment or advice but lack a valid prescription. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 10:2303-2311.
Symonds T, Dean JD, Carr A, Carlsson M, Marfatia A, and Schnetzler G (2011). A feasibility study comparing pharmacist and physician recommendations for sildenafil treatment. Journal of Sexual Medicine, 8:1463-1471.
Cooper RJ (2013). Over-the-Counter Medicine Abuse - a review of the literature. Journal of Substance Use, 18; 82-107.
Khan TM and Ibrahim Y (2013). A qualitative exploration of the non-prescription sale of drugs and incidence of adverse events in community pharmacy settings in the Eastern Province of the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. European Journal of Hospital Pharmacy, 20:26-31. doi: 10.1136/ejhpharm-2012-000161.
Bahnassi A (2014). Pharmacists views and practices in regard to sales of antibiotics without a prescription in Madinah, Saudi Arabia. Journal of Patient Safety, 12(3):159-164
Debaje SP and Hiremath RC (2014). Over the counter (OTC) sell of sex enhancer drugs: an emerging public health issue in India. International Journal of Research in Medical Sciences, 2:198-201. DOI: 10.5455/2320-6012.ijrms20140238.
Emeka PM, Al-Omar MJ and Khan TM (2012). A qualitative study exploring role of community pharmacy in the irrational use and purchase of nonprescription antibiotics in Al Ahsa. European Journal of General Medicine, 9; 230-234.
Gebregeorgise DT, Belay YM and Sporrong SK (2017). Sildenafil citrate use in Addis Ababa: characteristics of users and pharmacists' dispensing practices. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy, 40:67-73
Atikeler MK, Gecit I and Senol FA (2002). Optimum usage of prilocaine-lidocaine cream in premature ejaculation. Andrologia, 34:356-9.
Vic JM (2004). Specific aspects of erectile dysfunction and its treatment for community pharmacists. International Journal of Impotence
Research, 16: S50-S52.14. Smith KM and Romanelli F (2005). Recreational use and misuse of phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors. Journal of the American Pharmacists Association, 45:63-75.
Garba D, Abubakar IS, Yakasai IA and Magashi MK (2013). Use of aphrodisiacs amongst women in Kano, Northern Nigeria. IOSR Journal of Pharmacy, 01-04.
Yovwin D G, Imarhiagbe F A, Obazee E and Oguike T C (2015). Erectile dysfunction in a Sub-Saharan African population: profile and correlates in a tertiary care hospital. Sahel Medical Journal, 18:116-20.
Olugbenga-Bello AI, Adeoye OA, Adeomi AA and Olajide AO (2013). Prevalence of erectile dysfunction and its risk factors among adult men in a Nigerian community. Nigerian Postgraduate Medical Journal, 20: 130-5.
Adegun PT, Areo PO, Solomon A, Dada SA and Adebayo BP (2017). Erectile dysfunction in men with and without lower urinary tract symptoms in Nigeria. World Journal of Men's Health, 35(2): 107-114. https://doi.org/10.5534/wjmh.2017.35.2.107.
Braund R, Ratnayake K, Tong K, Song J, Chai S and Gauld N (2018). Pharmacist supply of sildenafil: pharmacists' experiences and perceptions on training and tools for supply. International Journal of Clinical Pharmacy. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11096-018-0622-z.
Amorha KC, Joda AE, Ayogu EE and Ubaka CM (2017). Community pharmacists' assessment of the factors that influence the recommendation of complementary medicines in Lagos state, Nigeria: a pilot study. West African Journal of Pharmacy. 28(1): 71-84.